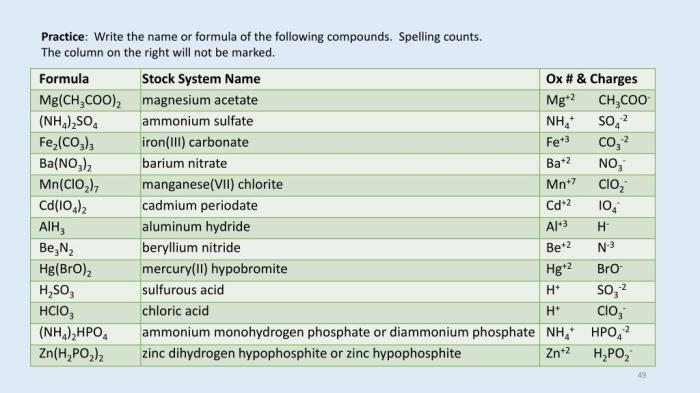
Ca h2po3 2 compound name – Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate, an intriguing compound with a multifaceted nature, takes center stage in this exploration. Its unique chemical structure and diverse applications across various industries make it a captivating subject for scientific inquiry and practical utilization.
From its role as a food additive to its significance in industrial processes and medical advancements, Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate’s versatility unfolds throughout this comprehensive guide, providing a panoramic view of its properties, synthesis, reactivity, and safety considerations.
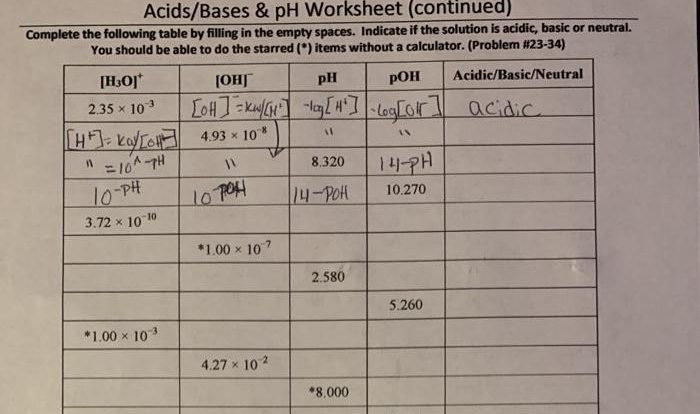
Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate: Ca H2po3 2 Compound Name

Calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate, also known as calcium dihydrogen phosphite, is a colorless, crystalline compound with the chemical formula Ca(H2PO3)2·2H2O. It is a salt of hydrogen phosphite and calcium.
Chemical Structure and Bonding
Calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate consists of calcium ions (Ca2+) and hydrogen phosphite ions (H2PO3-). The hydrogen phosphite ion is a polyatomic ion with the structure H-P-O-O-H. The calcium ions are coordinated to the oxygen atoms of the hydrogen phosphite ions, forming a network of bonds that hold the crystal structure together.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate is a white, crystalline powder that is soluble in water. It has a slightly acidic taste and is non-toxic. It is stable at room temperature and pressure, but it can decompose when heated to high temperatures.
- Molecular Weight:216.07 g/mol
- Melting Point:100 °C (decomposes)
- Solubility in Water:67 g/100 mL (20 °C)
- Acidity (pKa):2.12
Calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate is a reducing agent and can be used to reduce other compounds. It is also a weak acid and can react with bases to form salts.
Applications of Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate
Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate finds diverse applications in various industries, including food, industrial processes, medicine, and dentistry.
Food Additive and Preservative
In the food industry, Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate is used as an additive and preservative. It prevents the discoloration and spoilage of food products, extending their shelf life.
Industrial Processes
Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate plays a crucial role in industrial processes such as papermaking, textile manufacturing, and water treatment. In papermaking, it acts as a bleaching agent, enhancing the whiteness and brightness of paper. In textile manufacturing, it is used as a mordant, improving the dye’s adhesion to fabrics.
In water treatment, it removes impurities and reduces the formation of scale.
Medicine and Dentistry
Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate has applications in medicine and dentistry. In medicine, it is used as a calcium supplement and an antacid. In dentistry, it is employed as a component of dental cement and as a desensitizing agent to reduce tooth sensitivity.
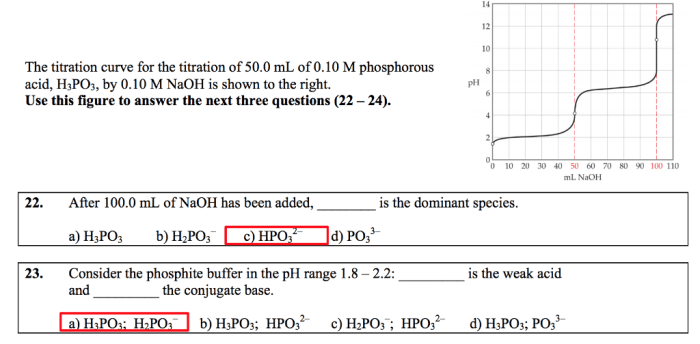
Production and Synthesis of Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate
Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate (CaH 2PO 3·2H 2O) can be synthesized through various methods. One common approach involves the reaction of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH) 2) with phosphorous acid (H 3PO 3).
This reaction can be carried out in aqueous solution at elevated temperatures and pressures. The resulting solution is then cooled and crystallized to yield CaH 2PO 3·2H 2O.
Factors Affecting Yield and Purity
Several factors can influence the yield and purity of CaH 2PO 3·2H 2O produced. These include:
- Reaction conditions:The temperature, pressure, and reaction time can significantly impact the yield and purity of the product.
- Stoichiometry:The stoichiometric ratio of calcium hydroxide to phosphorous acid must be carefully controlled to ensure complete reaction and minimize the formation of impurities.
- Impurities:The presence of impurities in the starting materials can lead to the formation of unwanted byproducts and reduce the purity of the final product.
Reactivity and Reactions of Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate
Calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate is a versatile compound that exhibits various reactions with acids, bases, and other chemicals. Its reactivity stems from the presence of hydrogen phosphite ions (HPO 32-), which can undergo proton transfer and redox reactions.
Reactions with Acids
Calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate reacts with acids to form calcium salts and phosphoric acid (H 3PO 4). The reaction proceeds as follows:
Ca(H2PO 3) 2·2H 2O + 2HCl → CaCl 2+ 2H 3PO 4+ 2H 2O
Reactions with Bases
When calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate reacts with bases, it undergoes a proton transfer reaction, forming calcium salts and hydrogen phosphite ions. The reaction is reversible and depends on the strength of the base:
Ca(H2PO 3) 2·2H 2O + NaOH → CaHPO 3+ NaH 2PO 3+ H 2O
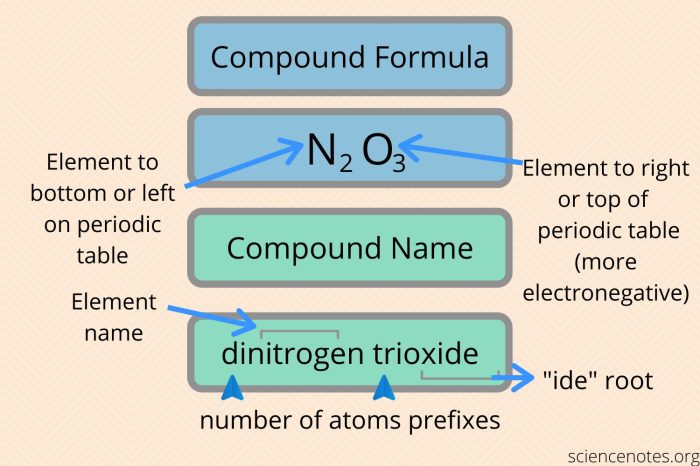
CaH2PO3 is a compound name that you might have come across in your AP Biology class. If you’re looking for more information on this topic, check out the ap bio frq 2016 answers for a comprehensive guide. Coming back to CaH2PO3, it’s worth noting that this compound is commonly known as calcium hydrogen phosphate.
Reactions with Other Chemicals
Calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate can also react with oxidizing agents, such as hydrogen peroxide (H 2O 2), to form calcium phosphate (Ca 3(PO 4) 2) and water:
Ca(H2PO 3) 2·2H 2O + 6H 2O 2→ Ca 3(PO 4) 2+ 6H 2O + 2H 3PO 4
Stability and Decomposition Pathways
Calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate is a relatively stable compound, but it can decompose under certain conditions. When heated to high temperatures, it undergoes thermal decomposition, releasing water and forming calcium metaphosphate (Ca(PO 3) 2):
Ca(H2PO 3) 2·2H 2O → Ca(PO 3) 2+ 3H 2O
Safety and Handling of Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate
Calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate is generally regarded as a low-toxicity compound. However, proper handling and storage procedures should be followed to minimize potential hazards.
Toxicity and Hazards, Ca h2po3 2 compound name
- Inhalation: Inhalation of dust or mist may cause irritation to the respiratory tract.
- Skin contact: Prolonged or repeated skin contact may cause irritation or dermatitis.
- Eye contact: Contact with eyes may cause irritation and redness.
- Ingestion: Ingestion of large amounts may cause gastrointestinal upset.
Handling and Storage
Calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate should be handled in a well-ventilated area. Avoid breathing dust or mist. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, eye protection, and a dust mask.
Store the compound in a cool, dry place away from incompatible materials, such as strong acids and bases.
Disposal and Environmental Considerations
Dispose of calcium hydrogen phosphite dihydrate in accordance with local regulations. Avoid releasing the compound into the environment.
FAQ Compilation
What is the chemical formula of Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate?
CaH2PO3·2H2O
What are the physical properties of Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate?
Colorless crystals, soluble in water, hygroscopic
What is the role of Calcium Hydrogen Phosphite Dihydrate in the food industry?
As a preservative, antioxidant, and yeast inhibitor