Homeostasis worksheet recognize normal parameters – Introducing the Homeostasis Worksheet: Recognizing Normal Parameters, an essential tool for healthcare professionals seeking to understand the intricacies of maintaining physiological balance. This worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of homeostasis, its mechanisms, and the significance of recognizing normal parameters in clinical practice.
Homeostasis, the body’s remarkable ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external fluctuations, is crucial for optimal health. Understanding normal physiological parameters, such as body temperature, blood glucose levels, and blood pressure, is paramount for assessing an individual’s health status and guiding appropriate interventions.
Introduction: Homeostasis Worksheet Recognize Normal Parameters
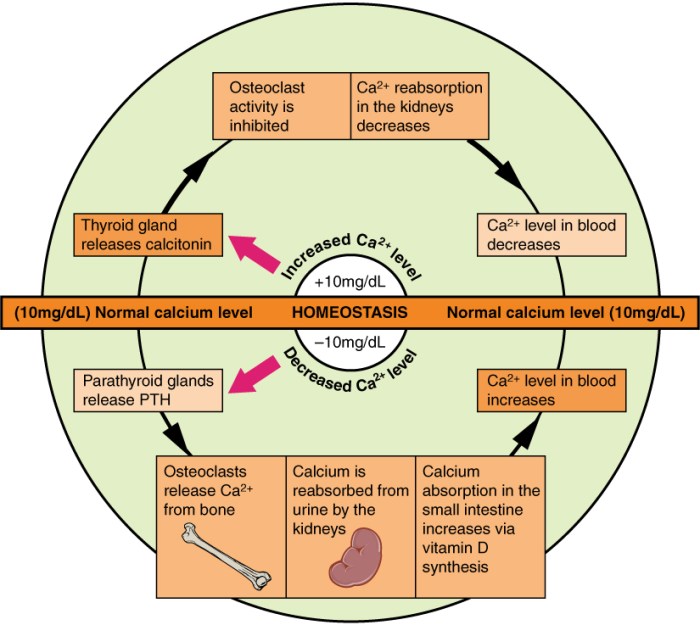
Homeostasis is the ability of an organism to maintain a relatively stable internal environment despite fluctuations in the external environment. It is a fundamental property of all living organisms, and it is essential for survival. Maintaining normal physiological parameters is crucial for optimal functioning and overall well-being.
These parameters include body temperature, blood glucose levels, pH levels, fluid balance, and blood pressure, among others.
Homeostasis Mechanisms
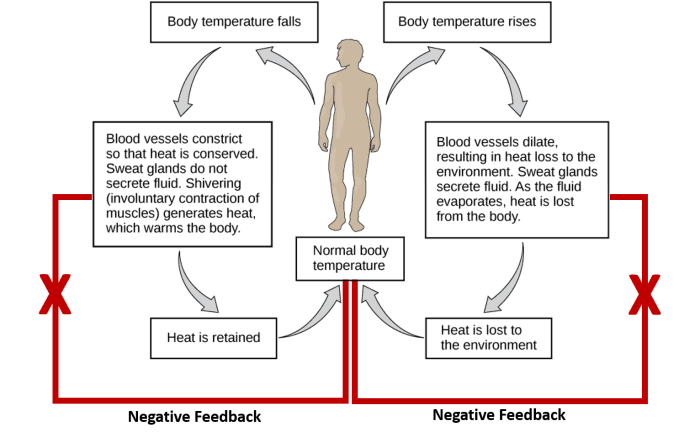
Homeostasis is maintained through a variety of mechanisms, including negative feedback loops and positive feedback loops. Negative feedback loops are the most common type of homeostatic mechanism. In a negative feedback loop, a change in a physiological parameter triggers a response that counteracts the change and brings the parameter back to its normal range.
For example, when body temperature increases, the body responds by sweating, which cools the body down. Positive feedback loops are less common than negative feedback loops. In a positive feedback loop, a change in a physiological parameter triggers a response that amplifies the change.
For example, the release of oxytocin during childbirth triggers contractions, which further stimulates the release of oxytocin, leading to stronger contractions.
Recognizing Normal Parameters, Homeostasis worksheet recognize normal parameters
Recognizing normal physiological parameters is essential for maintaining homeostasis. These parameters can be measured and monitored using a variety of methods, including blood tests, urine tests, and physical examinations. Reference ranges have been established for each physiological parameter, and these ranges can vary depending on factors such as age, gender, and health conditions.
Clinical Applications
Homeostasis worksheets are used in clinical settings to help healthcare professionals recognize normal physiological parameters and identify deviations from normal. This information can be used to diagnose and treat a variety of conditions. For example, a patient with a high blood glucose level may be diagnosed with diabetes, and a patient with a low blood pressure may be diagnosed with hypotension.
Monitoring physiological parameters is also important in patient care, as it can help healthcare professionals assess the effectiveness of treatment and identify potential complications.
Detailed FAQs
What is the purpose of a homeostasis worksheet?
A homeostasis worksheet is designed to guide healthcare professionals in recognizing and interpreting normal physiological parameters, which are essential for assessing an individual’s health status and guiding appropriate interventions.
How are normal physiological parameters established?
Normal physiological parameters are established through extensive research and clinical observations. Reference ranges are determined based on statistical analysis of data collected from healthy individuals.
What factors can affect normal physiological parameters?
Factors such as age, gender, health conditions, and environmental factors can influence normal physiological parameters. It is important to consider these factors when interpreting results.