Simple computations with impulse momentum change provide a fundamental framework for understanding the dynamics of objects in motion. By examining the relationship between impulse and momentum change, we uncover the principles that govern how external forces influence the motion of objects, with applications spanning diverse fields from physics to engineering.
This comprehensive guide delves into the concepts, methods, and applications of simple computations with impulse momentum change, empowering readers with the knowledge to solve complex problems and gain a deeper understanding of the physical world.
Simple Computations with Impulse Momentum Change
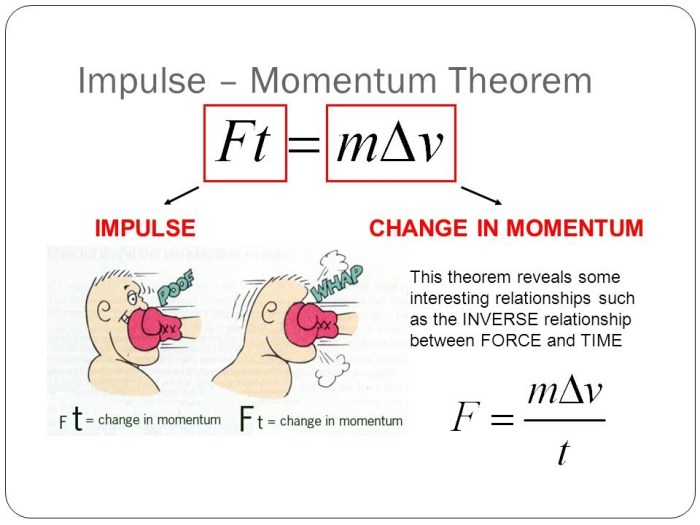
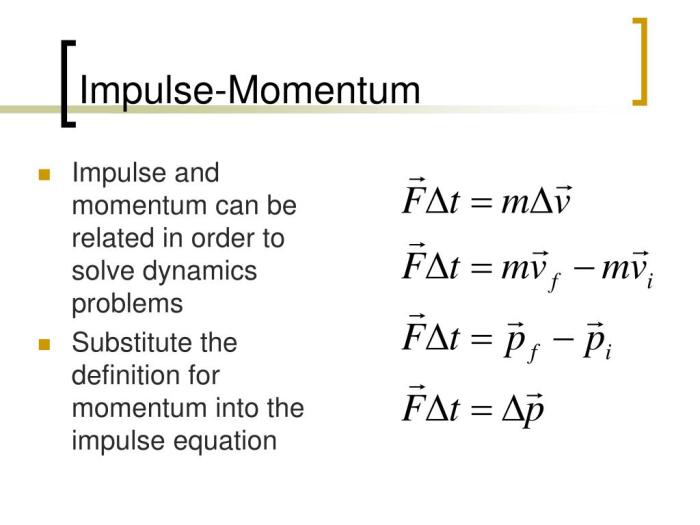
Impulse is a force acting over a short time interval, and momentum is the product of an object’s mass and velocity. Impulse momentum change is the change in momentum caused by an impulse. This concept is fundamental in understanding and analyzing interactions between objects in motion.
The relationship between impulse and momentum change is given by the formula: Impulse = Momentum Change (J = Δp)
Applications of Simple Computations with Impulse Momentum Change
- Calculating the force exerted by a baseball bat on a ball
- Determining the recoil of a gun
- Analyzing the impact of a car crash
- Designing airbags and other safety devices
Methods for Calculating Impulse and Momentum Change
Impulse can be calculated using the formula: Impulse = Force × Time (J = F × Δt)
Momentum change can be calculated using the formula: Momentum Change = Final Momentum – Initial Momentum (Δp = Pf – Pi)
Procedures for Solving Problems Involving Impulse Momentum Change
- Identify the objects involved and their initial and final velocities.
- Calculate the impulse acting on each object.
- Use the impulse-momentum change relationship to determine the momentum change of each object.
- Analyze the results and draw conclusions.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- Assuming that impulse and momentum are the same thing
- Ignoring the time interval over which the force is applied
- Using the wrong units for impulse and momentum change
Advanced Applications of Impulse Momentum Change, Simple computations with impulse momentum change
In astrophysics, impulse momentum change is used to study the dynamics of celestial bodies, such as the motion of planets and stars. In engineering, it is used to design and analyze structures that experience impact forces, such as bridges and buildings.
FAQ Section
What is impulse?
Impulse is the product of force and the time interval over which it acts.
What is momentum change?
Momentum change is the difference between the final and initial momentum of an object.
How are impulse and momentum change related?
Impulse and momentum change are related by the impulse-momentum theorem, which states that the impulse acting on an object is equal to the change in its momentum.
What are some applications of simple computations with impulse momentum change?
Simple computations with impulse momentum change are used in a wide range of applications, including the design of airbags, the analysis of car crashes, and the study of rocket propulsion.