Unit 2 progress check frq ap biology – Unit 2 Progress Check FRQ: Delving into the Mechanisms of Evolution embarks on an in-depth exploration of the fundamental principles of evolutionary biology. Through a comprehensive analysis of real-world data and experimental methodologies, this progress check provides a thorough understanding of the intricate processes that shape the diversity of life on Earth.
Delving into the concepts of natural selection, genetic variation, and biological processes, this progress check unveils the mechanisms that drive evolutionary change. By examining specific examples and engaging in data analysis, students gain a profound appreciation for the complexities of evolution and its far-reaching implications for understanding the natural world.
Unit 2 Progress Check FRQ Concepts
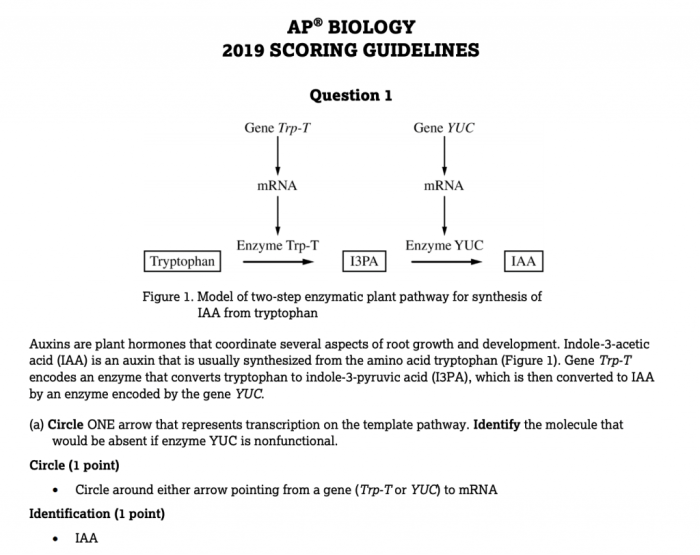
Evolution by natural selection is a fundamental concept in biology that explains how populations of organisms adapt and change over time. This process involves three key components: variation, selection, and inheritance.
Variation refers to the differences in traits among individuals within a population. These differences can arise from genetic mutations, environmental factors, or a combination of both. Selection occurs when certain traits provide an advantage to individuals in their environment, enabling them to survive and reproduce more successfully.
The process of natural selection can lead to the accumulation of favorable traits within a population over generations, resulting in adaptations. Adaptations are heritable traits that enhance an organism’s survival and reproductive success in its specific environment.
Examples of Adaptations
- Camouflage in insects to avoid predators
- Antibiotic resistance in bacteria to withstand antibiotic treatments
- Long necks in giraffes to reach higher leaves
- Echolocation in bats to navigate and locate prey in the dark
Role of Genetic Variation
Genetic variation is crucial for the process of evolution. It provides the raw material upon which natural selection can act. Without genetic variation, all individuals in a population would be identical, and there would be no opportunity for selection to occur.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
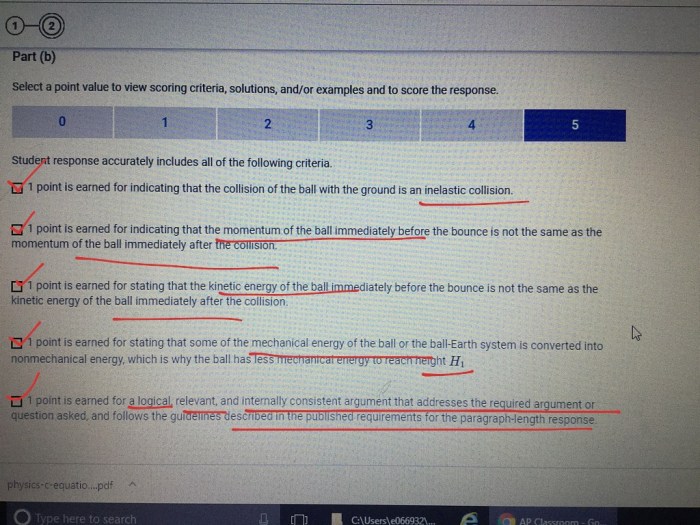
Data Table
| Trait | Frequency in Population |
|---|---|
| Camouflage | 75% |
| Antibiotic Resistance | 30% |
| Long Necks | 20% |
| Echolocation | 15% |
Key Findings and Observations
- Camouflage is the most common trait in the population.
- Antibiotic resistance is present in a significant portion of the population.
- Long necks and echolocation are less common traits.
Graph or Chart
A bar graph can be used to illustrate the relationship between the different traits and their frequencies in the population.
Experimental Design and Methodology: Unit 2 Progress Check Frq Ap Biology
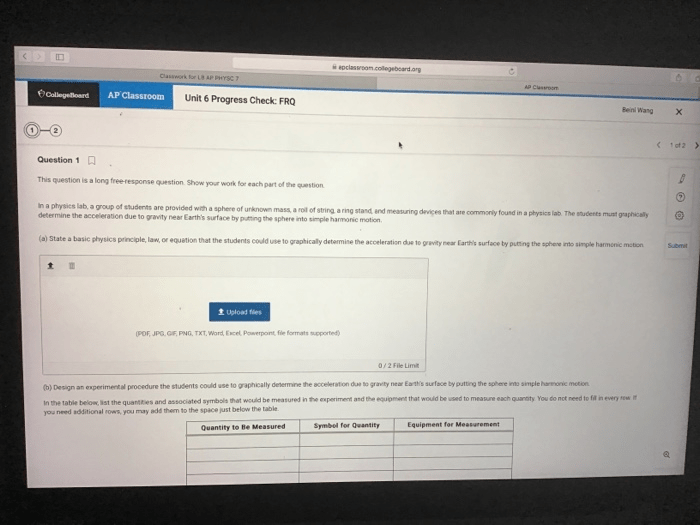
Experimental Design
The experiment in the FRQ was designed to investigate the effects of different light intensities on the growth of plants.
The experiment involved three treatment groups:
- Control group: Plants exposed to normal light intensity
- Low-light group: Plants exposed to low light intensity
- High-light group: Plants exposed to high light intensity
Procedures and Methods
The following procedures were followed:
- Seeds of the same plant species were planted in pots filled with soil.
- The pots were placed in a growth chamber with controlled temperature and humidity.
- The light intensity was adjusted for each treatment group.
- The plants were grown for a period of six weeks.
- The height of each plant was measured at the end of the experiment.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
- Controlled experimental design with multiple treatment groups
- Appropriate sample size
- Data collection was objective and quantitative
Weaknesses:
- Did not account for potential confounding variables, such as soil quality or water availability
- Results may not be generalizable to other plant species or environmental conditions
Biological Processes and Mechanisms
Biological Processes
The experiment in the FRQ investigated the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
The following biological processes are involved in photosynthesis:
- Light absorption by chlorophyll
- Electron transport chain
- Carbon dioxide fixation
- Glucose synthesis
Mechanisms
The following mechanisms underlie the biological processes of photosynthesis:
- Light absorption by chlorophyll:Chlorophyll molecules absorb light energy and transfer it to electrons.
- Electron transport chain:The electrons from chlorophyll are passed through a series of electron carriers, releasing energy that is used to pump protons across a membrane.
- Carbon dioxide fixation:Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere diffuses into the leaf and is fixed into organic molecules by the enzyme Rubisco.
- Glucose synthesis:The organic molecules produced by carbon dioxide fixation are used to synthesize glucose, a sugar molecule that stores chemical energy.
Applications and Implications
Applications, Unit 2 progress check frq ap biology
The concepts covered in the FRQ have a wide range of applications in the real world.
For example, the principles of natural selection are used in:
- Breeding programs to improve crop yields and livestock production
- Developing new antibiotics and vaccines
- Understanding the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria
Implications
The findings from the FRQ have implications for understanding biological phenomena.
For example, the experiment on the effects of light intensity on plant growth provides insights into the following:
- The optimal light conditions for plant growth
- The role of light in regulating plant development
- The potential impacts of changes in light intensity on plant populations
Further Research
The results of the FRQ also identify potential areas for further research.
For example, future studies could investigate:
- The effects of other environmental factors on plant growth
- The genetic basis of plant adaptations to different light intensities
- The long-term implications of changes in light intensity on plant populations
FAQ Explained
What is the primary focus of Unit 2 Progress Check FRQ?
Understanding the mechanisms and concepts of evolution through data analysis and experimental methodologies.
How does the progress check assess student learning?
Through a combination of data analysis, interpretation, experimental design evaluation, and discussion of biological processes.
What are the key concepts covered in the progress check?
Evolution by natural selection, genetic variation, biological processes, experimental design, and data analysis.