Acids bases & ph worksheet answer key – Welcome to the Acids, Bases, and pH Worksheet Answer Key, your ultimate resource for understanding the fundamental concepts of acids, bases, and pH. This guide provides clear and concise answers to commonly asked questions, making it an invaluable tool for students and professionals alike.
Acids, bases, and pH play a crucial role in various scientific disciplines, from chemistry and biology to environmental science and medicine. Understanding these concepts is essential for comprehending the behavior of chemical substances and their interactions with each other.
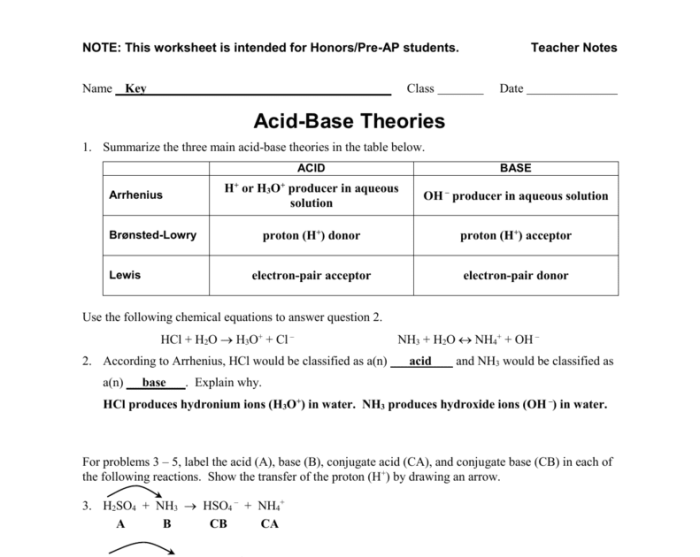
Acids, Bases, and pH: Acids Bases & Ph Worksheet Answer Key
Acids and bases are two fundamental classes of chemical compounds that exhibit distinct properties and play crucial roles in various chemical and biological processes.
An acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, releases hydrogen ions (H+) and lowers the pH of the solution. Acids typically taste sour, react with metals to produce hydrogen gas, and turn blue litmus paper red.
A base, on the other hand, is a substance that, when dissolved in water, releases hydroxide ions (OH-) and increases the pH of the solution. Bases typically taste bitter, feel slippery to the touch, and turn red litmus paper blue.
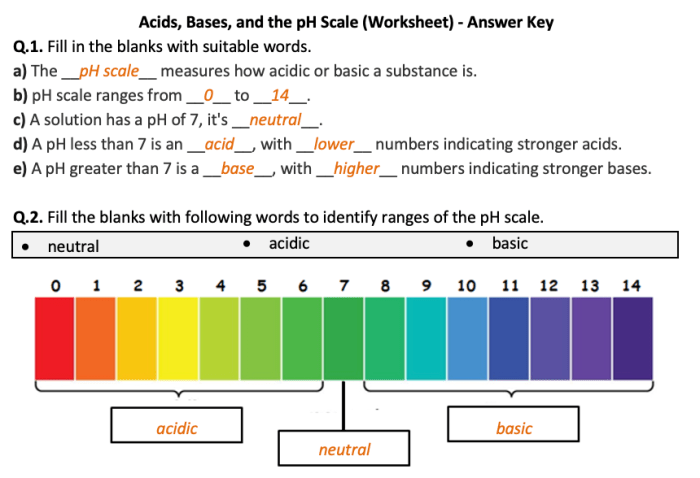
The pH scale is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A solution with a pH below 7 is acidic, while a solution with a pH above 7 is basic.
Common Acids and Bases
Some common examples of acids include:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
- Nitric acid (HNO3)
- Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
Some common examples of bases include:
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
- Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)
- Ammonia (NH3)
Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions are chemical reactions that involve the transfer of protons (H+) between an acid and a base. These reactions are important in many biological and industrial processes.
Neutralization
Neutralization is a specific type of acid-base reaction in which an acid and a base react in stoichiometric proportions to form a salt and water. The salt is a compound that contains the cation of the base and the anion of the acid.
The reaction of a strong acid with a strong base produces a neutral solution, while the reaction of a weak acid with a weak base produces a slightly acidic or basic solution.
Titration
Titration is a technique used to determine the concentration of an acid or base. In a titration, a known volume of an acid or base of known concentration is added to a solution of unknown concentration. The reaction between the acid and base is monitored using an indicator, which changes color when the reaction is complete.
The volume of acid or base added to reach the endpoint of the titration is used to calculate the concentration of the unknown solution.
Steps for Performing a Titration
- Fill a burette with the acid or base of known concentration.
- Add a known volume of the unknown solution to a flask.
- Add a few drops of indicator to the flask.
- Slowly add the acid or base from the burette to the flask, swirling constantly.
- Observe the color of the indicator.
- Continue adding the acid or base until the indicator changes color.
- Record the volume of acid or base added.
8. Calculate the concentration of the unknown solution using the following equation
“`Concentration of unknown solution = (Concentration of known solution
Volume of known solution) / Volume of unknown solution
“`
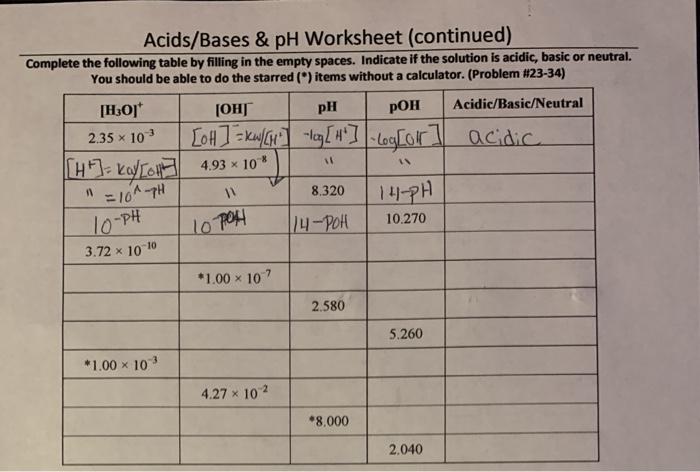
pH Calculations
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or basicity. It is calculated using the pH equation:
“`pH =
log[H+],
“`where [H+] is the molar concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
Buffer Solutions
Buffer solutions are aqueous solutions that resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added to them. They play a crucial role in maintaining the pH of biological systems, industrial processes, and environmental systems.
Types of Buffer Solutions, Acids bases & ph worksheet answer key
There are two main types of buffer solutions:
- Acidic buffers: Resist changes in pH when small amounts of base are added. They are composed of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
- Basic buffers: Resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid are added. They are composed of a weak base and its conjugate acid.
Applications of Buffer Solutions
Buffer solutions have numerous applications, including:
- Biological systems: Maintain the pH of blood, saliva, and other bodily fluids.
- Industrial processes: Control the pH of chemical reactions, such as in the production of pharmaceuticals and dyes.
- Environmental systems: Buffer the pH of lakes, rivers, and oceans, protecting aquatic life.
Applications of Acids, Bases, and pH in Everyday Life
Acids, bases, and pH play crucial roles in numerous industries and aspects of our daily lives. Their applications span a wide range from food preservation to medical treatments and manufacturing processes.
Food Industry
- Acids are used as preservatives in food products to inhibit microbial growth and extend shelf life. For example, citric acid is commonly added to fruit juices and canned goods.
- Bases, such as sodium bicarbonate, are used as leavening agents in baking to create a light and fluffy texture.
- pH is crucial in food processing, as it affects the flavor, texture, and safety of food products. For instance, the acidity of fruits and vegetables influences their taste and nutritional value.
Medical Field
- Acids are used in various medications, such as aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) for pain relief and hydrochloric acid for treating digestive disorders.
- Bases, such as antacids, are used to neutralize stomach acid and alleviate heartburn.
- pH is critical in maintaining the proper functioning of bodily fluids, such as blood and urine. Deviations from normal pH levels can indicate health issues.
Manufacturing
- Acids are used in metalworking to dissolve and remove impurities during surface treatment processes.
- Bases are used in the production of soaps, detergents, and paper.
- pH control is essential in wastewater treatment to neutralize harmful chemicals and ensure environmental safety.
Other Applications
- Acids are used in batteries to generate electricity.
- Bases are used in cleaning products to remove dirt and stains.
- pH is used in water quality monitoring to assess the safety and suitability of water for drinking, irrigation, and aquatic life.
Questions and Answers
What is the pH scale?
The pH scale is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, while values below 7 indicate acidity and values above 7 indicate alkalinity.
How do I calculate the pH of a solution?
The pH of a solution can be calculated using the pH equation: pH = -log[H+], where [H+] is the molar concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
What is a buffer solution?
A buffer solution is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. Buffer solutions are used to maintain a specific pH in various applications, such as in biological systems and chemical reactions.