Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of muscles of the upper arm quiz. This quiz will unravel the intricate anatomy, functions, and significance of these muscles, leaving you with a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating topic.
Delve into the depths of the biceps brachii and triceps brachii muscles, exploring their locations, functions, and the intricate interplay that enables elbow flexion and extension.
Muscle Anatomy of the Upper Arm
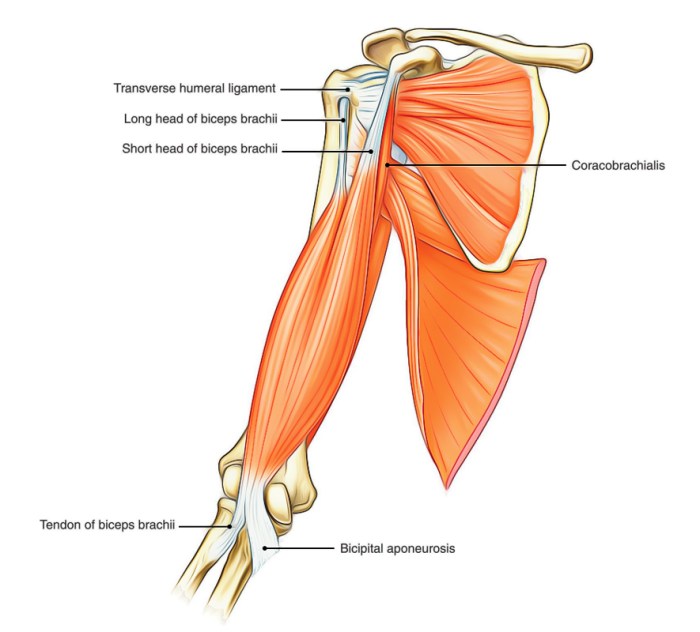
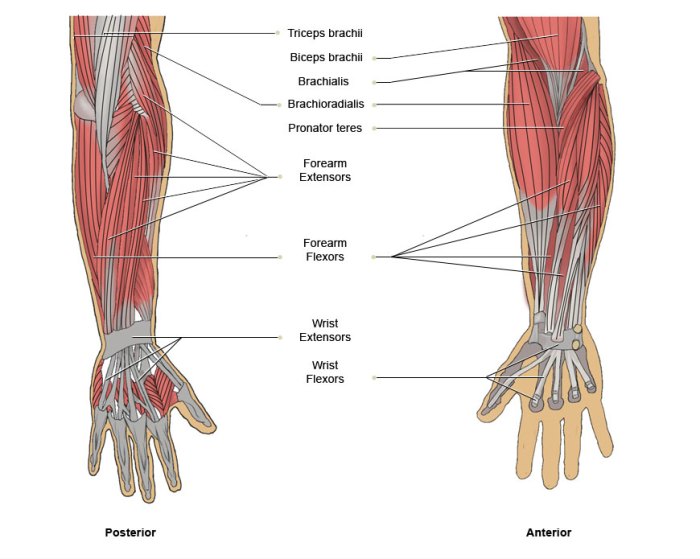
The upper arm, also known as the brachium, is the region between the shoulder and elbow. It contains several muscles that are responsible for various movements, including flexion, extension, and rotation of the forearm.
Biceps Brachii Muscle
The biceps brachii is a large, superficial muscle located on the anterior (front) side of the upper arm. It originates from two heads: the long head, which arises from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, and the short head, which originates from the coracoid process of the scapula.
The biceps brachii inserts into the radial tuberosity of the radius and the ulna tuberosity. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve.
Triceps Brachii Muscle
The triceps brachii is a large, three-headed muscle located on the posterior (back) side of the upper arm. The lateral head originates from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, the medial head originates from the humerus, and the long head originates from the scapula.
The triceps brachii inserts into the olecranon process of the ulna. It is innervated by the radial nerve.
Brachialis Muscle
The brachialis is a thick, deep muscle located on the anterior side of the upper arm. It originates from the distal half of the humerus and inserts into the coronoid process of the ulna. The brachialis is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve.
After a grueling workout targeting the muscles of the upper arm, a delicious treat is in order. Look no further than the tantalizing Bahama Breeze crab dip recipe . Its creamy texture and savory flavors will delight your taste buds, providing a perfect complement to your post-workout recovery.
Once you’ve indulged in this culinary masterpiece, don’t forget to return to the muscles of the upper arm quiz to test your knowledge on the intricate anatomy of this essential muscle group.
It is the primary muscle responsible for elbow flexion.
Muscle Actions and Movements: Muscles Of The Upper Arm Quiz
The muscles of the upper arm play a crucial role in various movements involving the elbow joint. Understanding their primary actions and how they work together is essential for effective upper body training and functional movements.
Biceps Brachii
The biceps brachii is a two-headed muscle located on the anterior (front) side of the upper arm. Its primary action is elbow flexion, which brings the forearm towards the upper arm.
Triceps Brachii
The triceps brachii is a three-headed muscle located on the posterior (back) side of the upper arm. Its primary action is elbow extension, which straightens the elbow joint.
Coordination of Elbow Flexion and Extension
The biceps brachii and triceps brachii work in coordination to perform elbow flexion and extension. During elbow flexion, the biceps brachii contracts, while the triceps brachii relaxes. Conversely, during elbow extension, the triceps brachii contracts, while the biceps brachii relaxes.
Exercises Targeting the Upper Arm Muscles, Muscles of the upper arm quiz
- Bicep Curls:Isolate the biceps brachii, targeting elbow flexion.
- Triceps Pushdowns:Focus on the triceps brachii, targeting elbow extension.
- Overhead Triceps Extensions:Engage the triceps brachii, emphasizing elbow extension with an overhead motion.
Muscle Attachments and Lever Systems
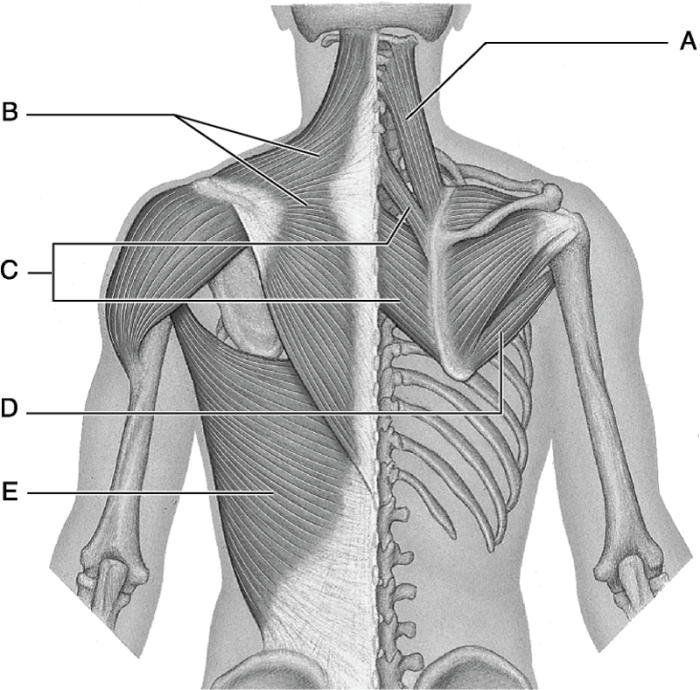
The muscles of the upper arm attach to various bones, including the humerus, scapula, and clavicle. These attachments determine the actions that each muscle can perform.
The elbow joint acts as a lever system, with the humerus serving as the lever arm. The muscles of the upper arm can act on this lever system to produce movement at the elbow.
Bony Attachments of the Upper Arm Muscles
- Anterior muscles:Biceps brachii (humerus and radius), brachialis (humerus and ulna), brachioradialis (humerus and radius)
- Posterior muscles:Triceps brachii (humerus and ulna), anconeus (humerus and ulna)
- Medial muscles:Pronator teres (humerus and radius), flexor carpi radialis (humerus and carpal bones)
- Lateral muscles:Supinator (humerus and radius), extensor carpi radialis longus (humerus and carpal bones)
Lever Systems of the Elbow Joint
The elbow joint acts as a hinge joint, allowing for flexion and extension. The muscles of the upper arm can act on this joint to produce these movements.
- Flexion:The biceps brachii and brachialis muscles act as flexors of the elbow joint.
- Extension:The triceps brachii muscle acts as an extensor of the elbow joint.
Table of Muscle Attachments and Lever Systems
| Muscle | Attachments | Lever System |
|---|---|---|
| Biceps brachii | Humerus and radius | Flexion |
| Brachialis | Humerus and ulna | Flexion |
| Brachioradialis | Humerus and radius | Flexion |
| Triceps brachii | Humerus and ulna | Extension |
| Anconeus | Humerus and ulna | Extension |
| Pronator teres | Humerus and radius | Pronation |
| Flexor carpi radialis | Humerus and carpal bones | Flexion and radial deviation |
| Supinator | Humerus and radius | Supination |
| Extensor carpi radialis longus | Humerus and carpal bones | Extension and radial deviation |
Muscle Strength and Conditioning
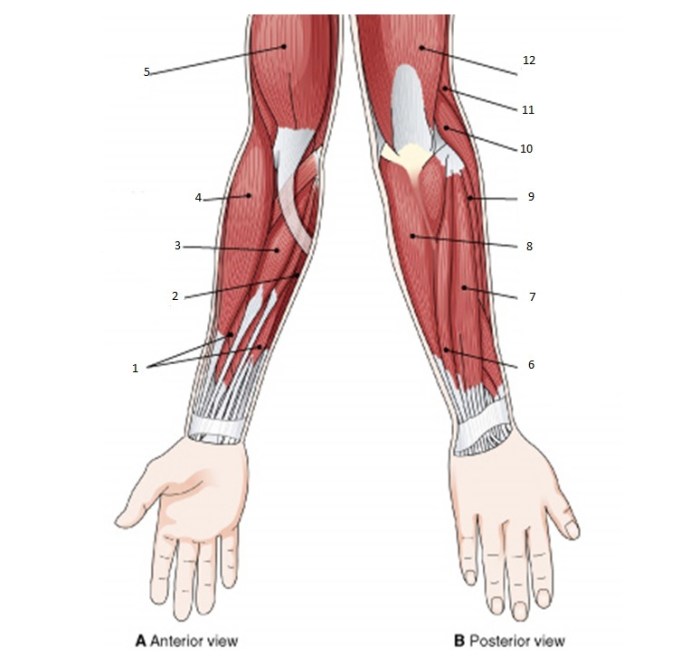
The strength of the muscles in the upper arm is influenced by various factors, including genetics, muscle fiber composition, training history, and age. Developing a comprehensive training program that incorporates progressive overload, proper technique, and adequate recovery is crucial for building muscle strength in the upper arm.
Training Guidelines
- Choose compound exercises:Exercises like push-ups, bench press, and tricep extensions work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, maximizing efficiency and promoting overall strength development.
- Incorporate progressive overload:Gradually increase weight, sets, or reps over time to challenge the muscles and stimulate growth.
- Maintain proper form:Focus on controlled movements with full range of motion to prevent injuries and maximize muscle engagement.
- Allow for adequate rest:Muscles need time to recover and rebuild; allow at least 48 hours of rest between workouts for each muscle group.
Recovery and Injury Prevention
Optimizing muscle recovery and preventing injuries is essential for long-term progress. Consider the following tips:
- Hydrate:Proper hydration aids in muscle recovery and prevents cramps.
- Consume protein:Protein provides the building blocks for muscle repair and growth.
- Sleep:Sleep is crucial for hormone production and muscle recovery.
- Warm up before workouts and cool down afterward:This helps prepare the muscles for exercise and reduces the risk of injuries.
- Listen to your body:If you experience pain, stop exercising and consult a healthcare professional.
Q&A
What is the primary function of the biceps brachii muscle?
Elbow flexion
How many heads does the triceps brachii muscle have?
Three
What is the role of the brachialis muscle?
Assists in elbow flexion